The foundation of each business is payroll, which forms the essential procedure for paying workers for their labor. In India, payroll has evolved significantly over the decades, influenced by regulatory complexity, economic growth, and rapid technological changes.
This article draws upon extensive experience in the payroll field to present an authoritative view of the past, present, and future of payroll in India, Freshers want to start a carrer in payroll domain and companies want to leverage payroll management.
The Genesis and Evolution of Payroll in India
- From Olden Days, payroll system in India was a highly manual and labor-intensive process.
- In early decades, typically prior to the 1990s, payroll was done using paper records and simple calculations. Salary slips were handwritten or typed, and statutory compliance like Provident Fund (PF) and Employee State Insurance (ESI) filing were manual and prone to errors.
- The complexity of Indian labor laws made payroll a challenging undertaking for businesses with growing workforces.
- With the economic liberalization in the 1990s, India witnessed rapid industrial growth and entry of multinational companies.
- This created a need for more structured and scalable payroll systems that could ensure accuracy, timeliness, and compliance.
- The early 2000s saw the introduction of computerised payroll systems and spreadsheets, even though many companies at that time used to operate on manual processes.
- Over time, payroll started to integrate more systematically with HR and finance functions.
How Technology Transformed Indian Payroll
- The real transformation in payroll came with the advent of dedicated payroll software and automation tools in the last 15 years.
- Solutions like SAP, Oracle, ADP, and Indian homegrown platforms such as Keka, GreytHR, and Zoho Payroll emerged to automate salary processing, deductions, tax calculations, and statutory compliance.
- Cloud technology further changed the payroll environment by allowing businesses to process payroll remotely/ work from home with real-time access and security. Cloud payroll platforms made it easier to update tax forms and laws that the Indian government requires, which are subject to frequent modifications.

The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Payroll
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning are the newest frontiers reshaping payroll management in India:
- Compliance Automation: AI tracks legislative updates automatically and adjusts payroll calculations for PF, ESI, TDS, and professional tax accordingly, eliminating the risk of missing regulatory changes.
- Error Detection: Artificial intelligence analysis payroll data and segregate information such as duplicate entries, incorrect overtime claims, or inconsistent deductions, checking corrections before payroll finalization.
- Real-time Salary Calculations: Integration of AI with attendance and HR systems allows payroll to be continuously updated for leaves, bonuses, or reimbursement changes without waiting for end-of-month processing.
- Employee Self-Service & AI Chatbots: Employees now have 24/7 access to payroll info via chatbots that can instantly answer queries about payslips, deductions, tax, and compliance details, reducing HR workload.
- Predictive Payroll Analytics: AI forecasts payroll costs, cash flow needs, and workforce trends, helping management make strategic decisions.
The adoption of AI-driven payroll ensures higher accuracy, faster processing, regulatory compliance, and improved employee satisfaction compared to traditional methods.
Popular Payroll Software in India in 2025
India’s payroll software market is dynamic, with products tailored to businesses of all sizes. Leading solutions include:
- Darwinbox: An end-to-end HR and payroll platform known for comprehensive automation and compliance management.
- Keka: It changed the payroll industry with new options like statutory compliance features and combined payroll with attendance.
- GreytHR: Popular for SMEs, focusing on ease of use and statutory compliance.
- Zoho Payroll: Cloud-based payroll software with self-service portals and tax filing integration.
- SAP Success Factors and Oracle HCM: Enterprise-class global payroll systems used by large multinationals.
- ADP India: A global payroll and compliance solution provider with cloud capabilities for Indian businesses.
These software platforms continuously evolve incorporating AI and cloud benefits to meet regulatory changes and workplace demands.

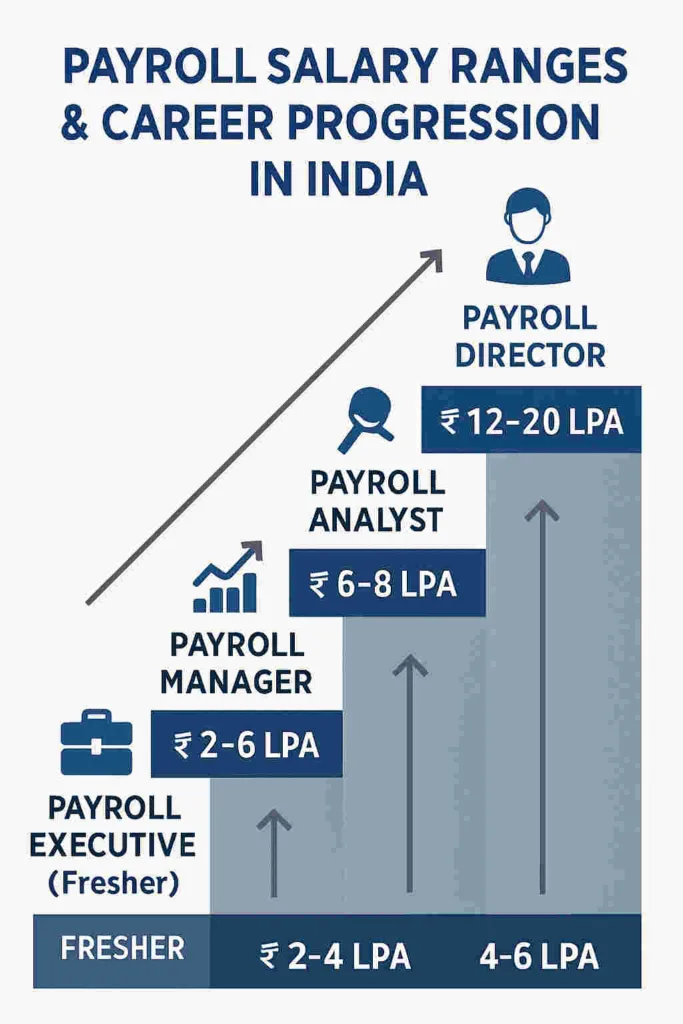
Payroll Jobs and Career Progression in India
With positions ranging from beginning to leadership, payroll provides a defined career path:
- Payroll Trainee/Assistant: Freshers begin here, learning payroll processing, data entry, and compliance basics.
- Payroll Executive: Handles day-to-day payroll operations, calculations, and statutory filings.
- Payroll Specialist/Analyst: Focuses on payroll audits, compliance analysis, and handling complex payroll scenarios.
- Payroll Manager: supervises payroll staff, oversees compliance with regulations, and connects payroll team with finance and human resources.
- Payroll Consultant/Director: Provides strategic payroll policy advice and manages payroll transformation projects.
The domain blends finance, human resources, and IT insights, enabling professionals to build a versatile skill set
| Role | Experience | Salary Range (INR) |
|---|---|---|
| Payroll Trainee | Fresher | ₹1.5 - ₹3.0 lakh per annum |
| Payroll Executive | 1-3 years | ₹3.5 - ₹6.0 lakh per annum |
| Payroll Specialist | 3-6 years | ₹6.0 - ₹12.0 lakh per annum |
| Payroll Manager | 6+ years | ₹10.0 - ₹20.0 lakh per annum |
| Senior Payroll Lead | 10+ years | ₹20.0 - ₹50.0 lakh per annum |
Freshers entering payroll typically start as Payroll Assistants or Trainees with salaries around ₹1.5 to ₹3 lakh per annum. With certifications and experience in technologies like SAP Payroll or AI-based platforms, mid-career professionals can significantly increase compensation.
Key Compliance and Regulatory Factors in Indian Payroll
Indian payroll is closely governed by central government and state governments laws:
- Payment of Wages Act (1936): prioritises the timely payment of wages without unauthorized deductions.
- Minimum Wages Act (1948): Mandates minimum wages based on region and skill.
- Employees’ Provident Fund Act (EPF -1952): Oversees PF deductions/contributions in any establishments.
- Employee State Insurance (ESI) Act (1948): Covers health insurance benefits.
- Tax Deducted at Source (TDS): Payroll must deduct income tax from salaried employees monthly.
- Professional Tax: State-level tax applicable in many states.
Running payroll compliantly requires constant updates, which modern payroll software and AI automation handle efficiently.
Why Payroll is a Promising Career for Freshers in India
- Job Stability: Payroll is critical to businesses; demand remains consistent irrespective of economic cycles.
- Growing Opportunities: Widespread digitization means more companies require skilled payroll professionals familiar with automation and compliance.
- Skill Development: Payroll professionals develop expertise in finance, labor laws, software platforms, and analytics.
- Good Compensation Potential: Salaries grow with certification (e.g., Certified Payroll Professional) and experience.
- Global Career Mobility: Knowledge of global payroll systems and regulations can open international roles.
Conclusion
- Payroll in India has transitioned from manual, error-prone processes to sophisticated AI-driven, cloud-based systems that streamline employee compensation management while ensuring regulatory compliance.
- For freshers, payroll is an excellent entry point into the corporate world, offering solid job security, learning opportunities, and salary growth.
- Investing time in understanding Indian labor laws, mastering payroll software, and staying updated with artificial intelligence applications will prepare professionals to excel in this essential and evolving domain.








